The Eliko RTLS is an on-premise real-time tracking system based on Ultra Wide Band radio technology (UWB). It consists of different hardware, software and accessories. The core elements of the system are anchors, tags and the RTLS Ranging software. Depending on the use case and configuration of the system, Eliko may provide additional devices for the communication network, server hardware or device accessories. Here is a high-level view of the Eliko RTLS architecture.

The Eliko RTLS network devices: anchors and tags
The anchors form the UWB RTLS network infrastructure and can be installed on any suitable structural component in or around the tracked area, such as walls, poles, and the ceiling. The tags come in different form factors and are suitable for tracking any object or person. Most often, the RTLS is used for tracking people, moving machinery, semi-finished goods or other assets. For a more detailed technical specifications of the Eliko RTLS devices please check the technical specifications of the UWB anchors, personnel tags and asset tags.

The Eliko RTLS is based on the active-passive two-way ranging (AP-TWR ) UWB protocol that enables to build robust and highly accurate UWB networks.
How AP-TWR ranging works?
-
The tags and the anchors communicate over UWB so that the tags initiate and also respond to the anchors. This is called two-way ranging (TWR) communication.
-
The TWR measures the time-of-flight (ToF) of the radio signal between the devices.
-
The system then uses a combination of these ToF measurements from both active (responding) and passive (listening) anchors. Hence, the protocol is called active-passive two way ranging or AP-TWR.
-
The ToF measurements are converted into distances and the anchors communicate the distances to the RTLS Ranging software via a wired or a wireless connection.
-
If a wired connection is used then the power connection is done over the Power over Ethernet (PoE).
-
-
In addition to the distances, the following data can be exchanged over the same UWB radio interface:
-
The AP-TWR protocol commands sent from the RTLS Ranging software to the tags and the feedback from the tags to the RTLS Ranging software;
-
The alarms sent from the tags to the RTLS Ranging software;
-
The Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) data from the asset tags, i.e. acceleration and angular velocity sent as auxiliary data within the UWB packets. Currently the portion of auxiliary data is limited to 16 bytes in uplink packets (from the tags to the anchors) and 4 bytes in downlink packets (from the anchors to the tags).
-
The Eliko RTLS software components and services
The core software components of the Eliko RTLS include the RTLS Ranging software, the Eliko RTLS Manager and the API integration layer. A high-level view of the Eliko RTLS software components is given below in Figure 2.3.
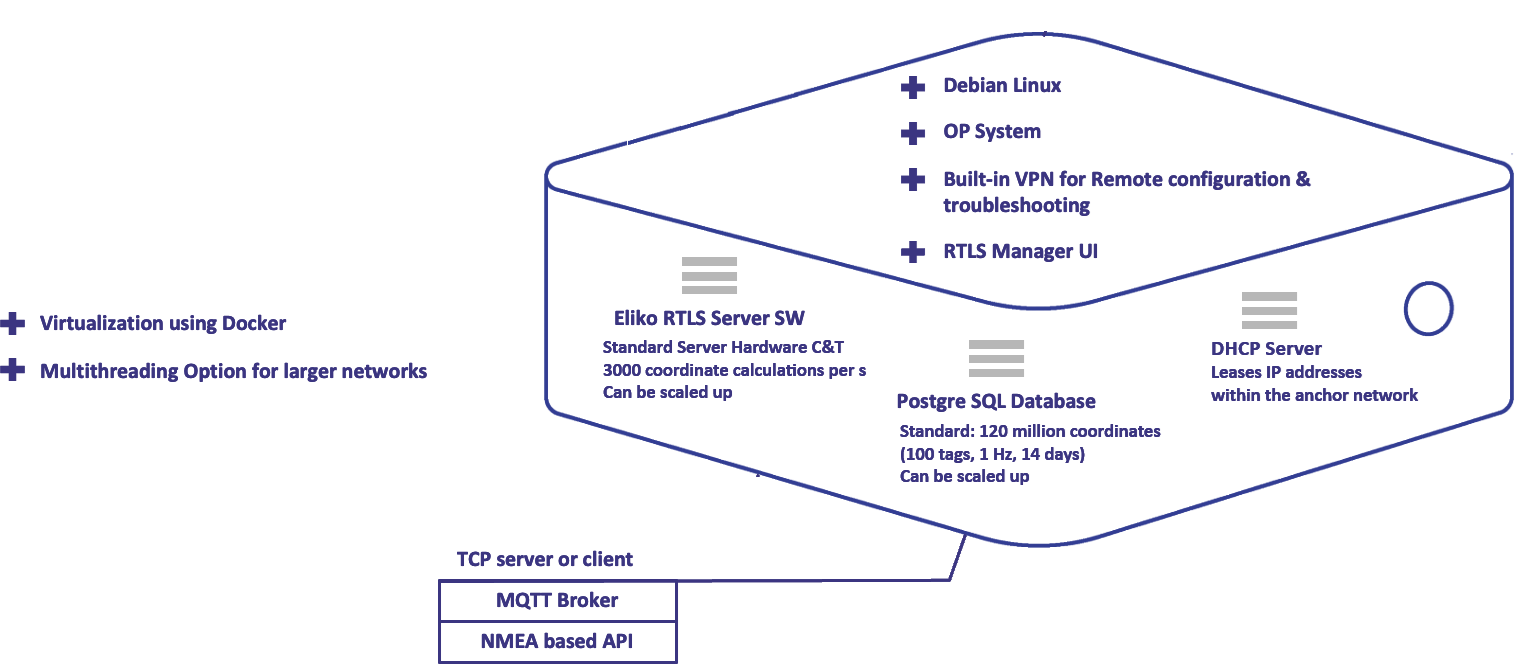
The Eliko RTLS Ranging software running on a local server can be hosted on Eliko provided server hardware or virtualized. It joins the data together and computes the tag’s coordinates based on the reported tag distances and known anchor coordinates. In its standard dedicated server setup the hardware is capable to perform up to 3000 coordinate calculations per second but this number can be further scaled up if customization is needed. The Eliko technical team will configure the coordinate filters according to the customer application needs. There is a trade off between coordinate latency and the “smoothness” of the tracked objects coordinates - there is a optimum for each application. The Eliko RTLS system also uses self-learning algorithms which based on the coordinate calculation determine if the input data is correct and will recalculate the coordinate with improved input data.
After calculation and post-processing of coordinates, the Eliko RTLS Ranging software makes the location information - including coordinates and distances - available for the integration to the customer application through a live data stream (TCP/IP). The data stream can also be configured from the customer application side. In addition to the localisation information, the Eliko RTLS Ranging software enables to create zones and geofences, create zone-based events to the third party systems using MQTT and configure real-time alarms to tags – both using visual light and vibration.
The basic system configuration can be done through the Eliko RTLS Manager GUI software, while more advanced configuration is done through the proprietary NMEA-based API:
-
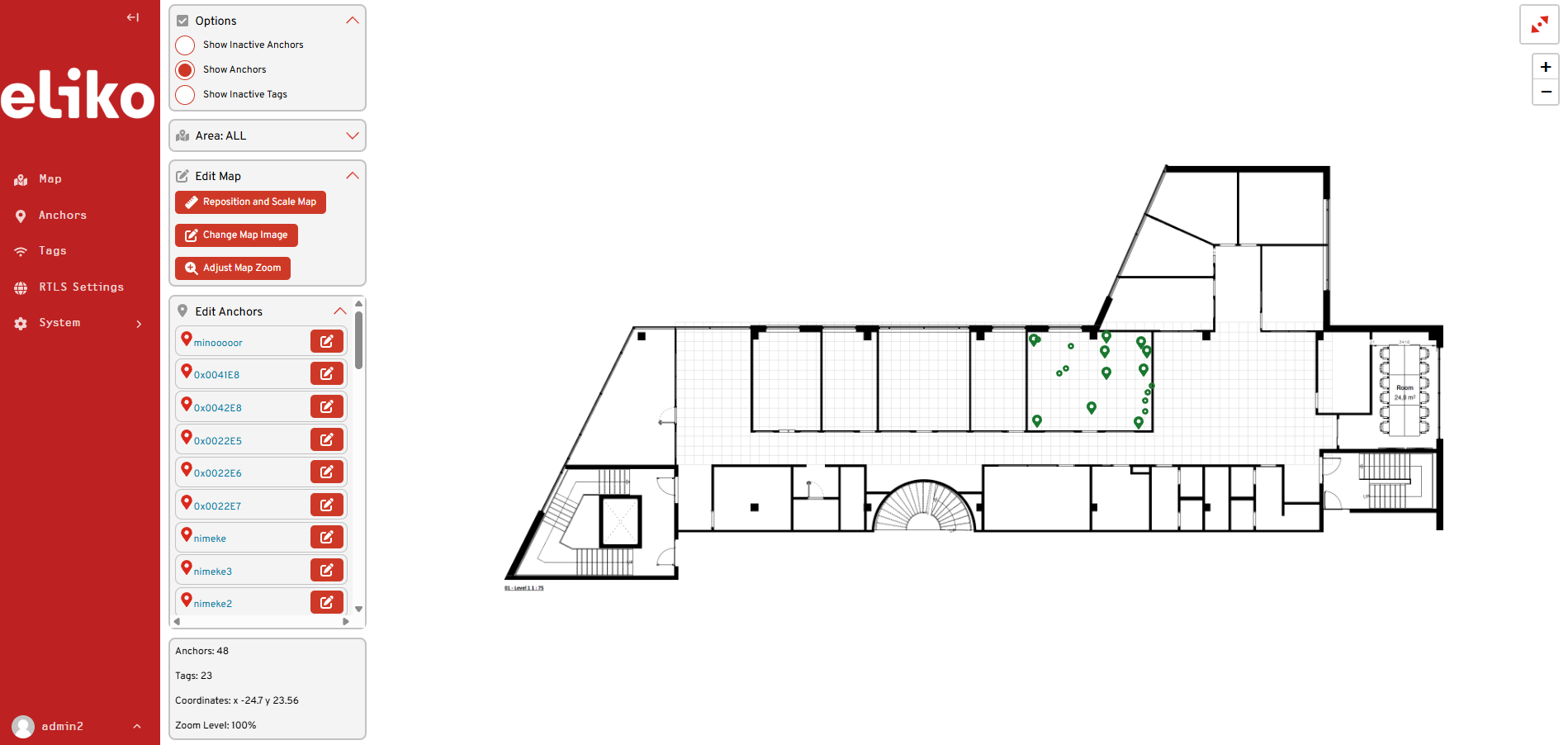
The Eliko RTLS Manager communicates with the Eliko RTLS Ranging software to visualize and monitor the system in real time. It is a web-based GUI, which enables users to monitor tag battery levels, configure positioning mode, update rates and aliases for tags, insert anchor coordinates and visualize both anchors and tags on a floorplan map. A map view of Eliko RTLS Manager GUI is shown in Figure 2.4.
-
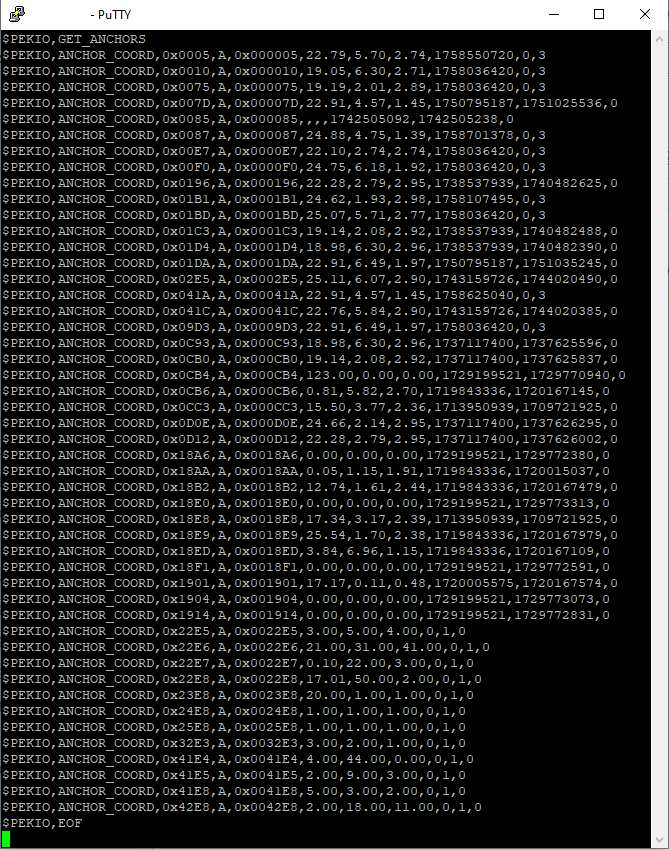
The Eliko API is based on sentences in the NMEA format. It allows users to configure all the system parameters (including geofences and events), receive tag coordinates in real time and set up the location data flows to the third party applications. To configure using API commands you have to connect to the RTLS Server via a terminal window (e.g. PuTTY) as shown in Figure 2.5. For more details about the Eliko API please refer to the API manual.
The RTLS Ranging Software configuration and measurement data are kept in an internal Postgre SQL Database. The standard configuration enables the database to host up to 120 million records (e.g. a 14-day history period for 100 tags with 1 Hz reporting frequency) but it can be further scaled up if customization is needed.
The RTLS software layer also includes components for managing the anchor network, i.e. running a DHCP server and leasing the IP addresses to the anchors.
The Eliko RTLS implementation options
The Eliko RTLS positioning is suitable for:
-
A standalone implementation for simple real-time positioning. In this case, you can use the RTLS Manager GUI to visualise the tags on the floor plan of the tracking area and configure basic RTLS settings, including anchor coordinates, tag positioning mode and reporting intervals. For more complex settings, it’s necessary to use a terminal (e.g. PuTTY) to send NMEA API commands to the RTLS Ranging software.
-
An integration with other software via the Eliko RTLS API (ERP, MES, etc.) either directly or through integration platforms.
-
A custom solution where positioning is integrated into the client’s product. For example, in immersive gaming, the tags can be integrated into wrist bands or other gaming equipment. The live coordinates and geofence data can be streamed into the customer’s application, where players' identity and position is used for enabling live user-specific experiences.
The Eliko RTLS in facts and numbers
-
The coordinate accuracy is 30 cm on average, but can be as high as 5 cm when the anchors are directly visible to tag.
-
The range of one anchor can be up to 50 meters on UWB channel 5 in direct visibility (line-of-sight).
-
An area of 25 x 25 meters can be covered in direct visibility with 4 anchors on UWB channel 5
-
The positioning frequency is freely adjustable from several minutes to 75Hz for a personnel tag.
-
In an area bounded by 4 anchors, the maximum number of positioning reports over the UWB radio channel in perfect line-of-sight conditions is 320 per second, i.e., 320 tags can be positioned once per second.
-
In the standard dedicated server hardware setup, the RTLS Ranging software can handle positioning traffic from multiple anchor areas with total intensity of up to 3000 ranging reports per second.
-
The coordinate calculation and transmission has a very low latency of 10-20 ms (depending on the configuration).
-
In addition to ranging, the asset tags can also transmit up to 16 bytes of IMU data (acceleration and angular velocity in X, Y and Z axis dimensions) per UWB packet.
-
The positioning can be freely extended to different floors and buildings.
-
We use two-way communication between the tag and the anchors, i.e., we can also send messages to the tag (turn on the LED, buzzer, and additional devices if necessary).
-
The Eliko RTLS Ranging software runs on an on-premise server and does not require an external internet connection making is very secure. However, external access to the server is required for the optional remote monitoring service.
-
All technology, from the AP-TWR protocol to hardware and software, is developed in-house.
